![]()
The 5 Point Plan Overview: Joining Linux Mint to Active Directory (Windows Server 2022)
Step 1: Network & DNS (The Foundation)
Before touching any domain commands, the Linux machine must "see" the world exactly as the Domain Controller does.
- Action: Set a static IP (e.g., 172.27.176.32).
- The "Why": Linux uses DNS SRV records to find the DC. If your DNS points to a router or Google (8.8.8.8) instead of your DC (172.27.176.34), the realm join will fail or become "intermittent," which is a primary cause of future 1311 errors.
- Verification: Run ping server2022.local. It must resolve to the DC IP.
Step 2: The Domain Join (The Handshake)
Use the realm tool. It is the modern "human-method" because it automatically configures Kerberos (krb5.conf) and SSSD for you.
- Action: sudo realm join -U Administrator server2022.local
- The "Why": This creates the computer object in Active Directory and negotiates the initial "Machine Password."
- Note: If you have re-installed Mint multiple times, you must "Reset Account" on the computer object in the Windows AD console first to ensure the Key Version Number (KVNO) starts at a clean state.
Step 3: SSSD Hardening (The Security Gate)
The System Security Services Daemon (SSSD) handles the actual "Who are you?" requests.
- Action: Ensure /etc/sssd/sssd.conf is owned by root:root and set permissions to 600.
- sudo chmod 600 /etc/sssd/sssd.conf
- The "Why": SSSD handles sensitive Kerberos keys. If the file is readable by anyone else, the service will refuse to start for security reasons. This is often why the service fails after a manual edit.
Step 4: Samba Configuration (The File Bridge)
Samba needs to be told to "step back" and let SSSD handle the identities.
- Action: In smb.conf, set security = ADS and workgroup = LABSERVER2022.
- The "Why": A common "revelation" error is having both security = ADS and security = user. This creates a conflict that crashes the SMB service.
- The "Secret" Line: Add kerberos method = secrets and keytab. This forces Samba to use the same "passport" that SSSD just created during the join, preventing 1311 "Domain Unavailable" errors.
Step 5: Authentication & Mapping (The Validation)
Windows Server 2022 is stricter about how it verifies targets than previous versions.
- Action: Always attempt the initial map using the Hostname: net use Z: \\MINT-SRV\Share.
- The "Why": When you use an IP address, Kerberos (the secure protocol) often fails because it can't "prove" the IP belongs to the server, leading to Error 1311. By using the Hostname, you force a proper ticket exchange.
- Service Check: Always run systemctl status sssd smbd to ensure the "lights are on" before trying to map.
Final Troubleshooting Note for the .docx
If "System Error 1311" appears:
- Check Time: Run date on Mint and check the clock on the DC. They must be within 5 minutes of each other.
- Clear Tickets: On Windows, run klist purge before retrying the map.
Would you like me to provide the exact, finalized text for the sssd.conf and smb.conf files to go along with this 5-step guide?
1. Network Configuration (Internal LAN)
Before joining the domain, Mint must be able to resolve the Domain Controller's SRV records.
- IP Address: 172.27.176.32
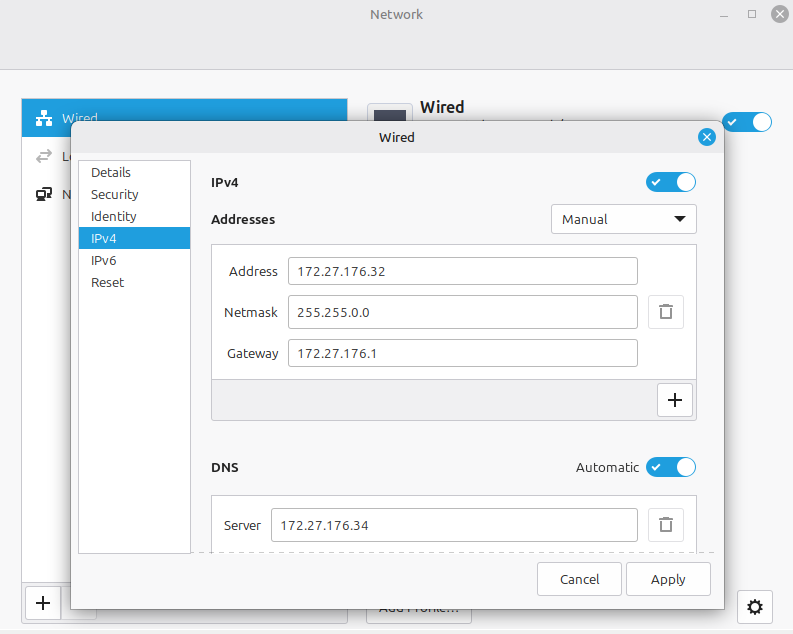
- Netmask: 255.255.0.0 (for /16)
- Gateway: 172.27.176.1 (Laptop Inet Bridge)
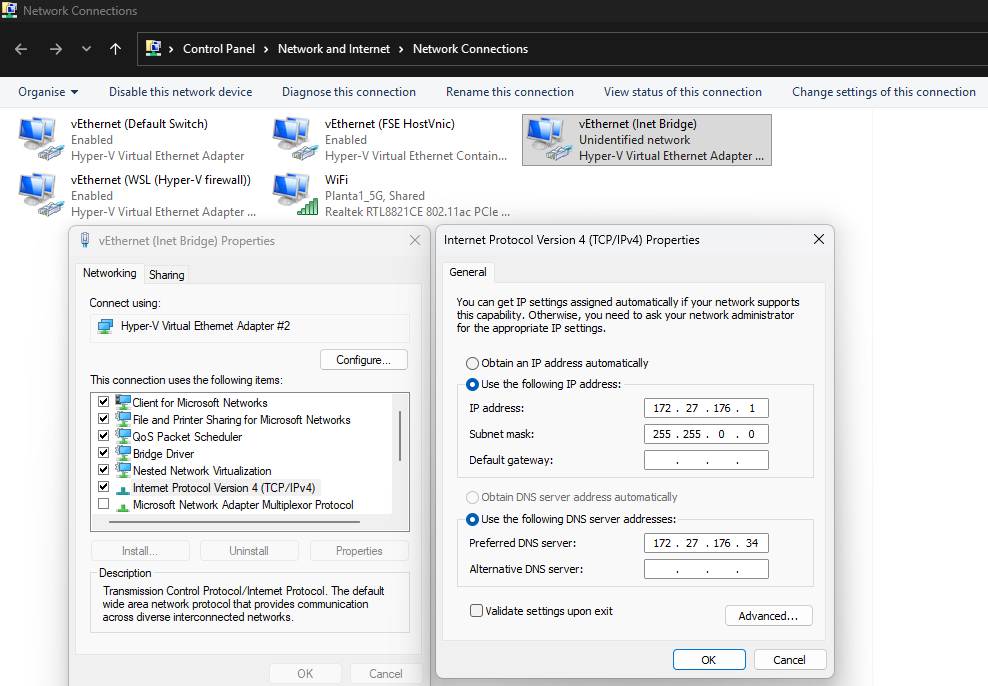
- DNS Server: 172.27.176.34 (The DC)
- Note: Ensure the DC is the only DNS server listed to prevent lookups from leaking to an external DNS that doesn't know about server2022.local.
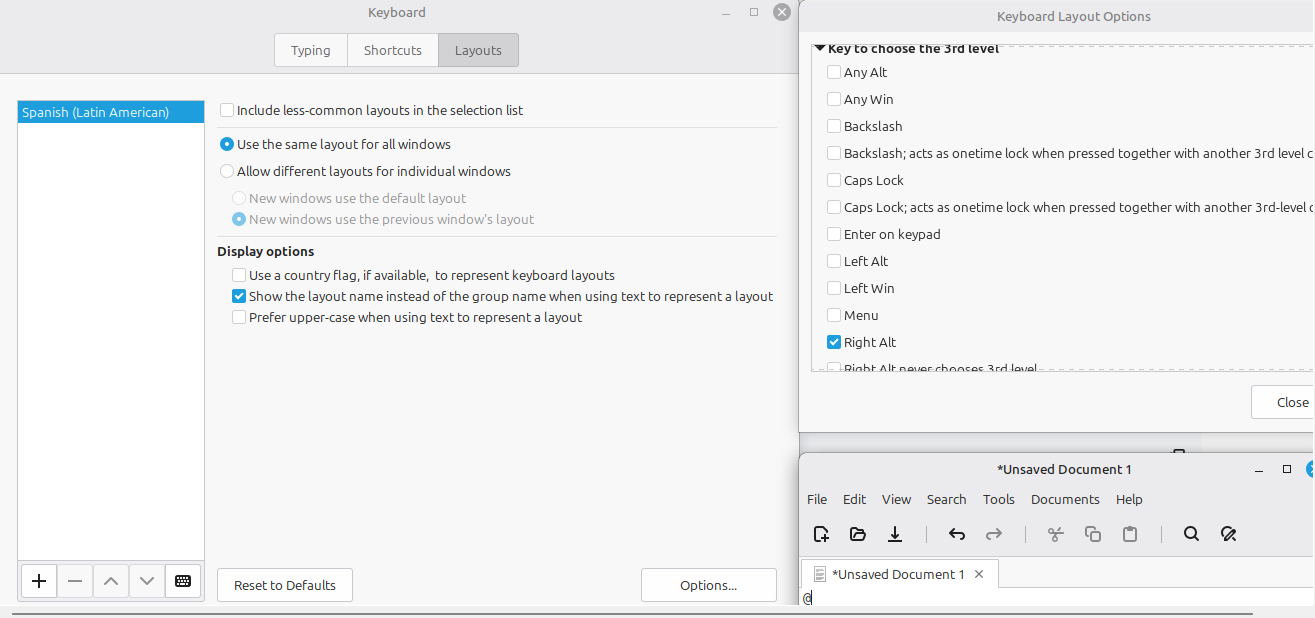
2. Keyboard Setup (Latam/Colombia)
To ensure the @ symbol (AltGr + Q) works for entering domain credentials:
- Open Menu -> Keyboard -> Layouts.
- Add Spanish (Latin American).
- Click Options... -> Expand Key to choose 3rd level.
- Select Right Alt (AltGr).
- Test the @ symbol in the terminal before proceeding.
3. Domain Stack Installation (SSSD Only)
We are excluding winbind entirely to prevent "System Error 1311" and identity conflicts.
Bash
sudo apt update
sudo apt install -y sssd-ad sssd-tools realmd adcli krb5-user samba-common-bin
4. Join the Active Directory Domain
Ensure the hostname is set correctly, then join using the Domain Administrator.
Bash
sudo hostnamectl set-hostname mint-srv
steve@MintVM:~$ sudo realm join -U Administrator sbs.server2022.local
Password for Administrator: xxxxxxxxxx
steve@MintVM:~$
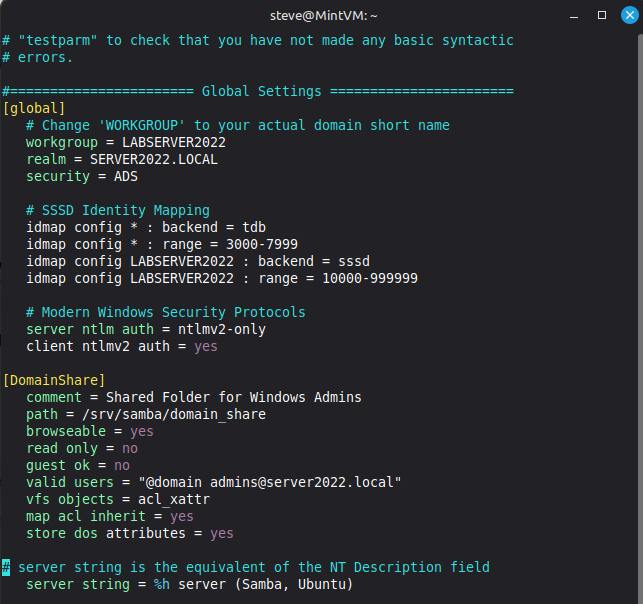
5. Samba Configuration (/etc/samba/smb.conf)
Critical: You must manually update the [global] section to replace the default WORKGROUP with your actual Domain NetBIOS name.
NB! This NETBIOS name was a pasted error at the VM install, so stuck with it as a core property of the DC.
Plaintext
[global]
# Change 'WORKGROUP' to your actual domain short name
workgroup = LABSERVER2022
realm = SERVER2022.LOCAL
security = ADS
# SSSD Identity Mapping
idmap config * : backend = tdb
idmap config * : range = 3000-7999
idmap config LABSERVER2022 : backend = sssd
idmap config LABSERVER2022 : range = 10000-999999
# Modern Windows Security Protocols
server ntlm auth = ntlmv2-only
client ntlmv2 auth = yes
[DomainShare]
comment = Shared Folder for Windows Admins
path = /srv/samba/domain_share
browseable = yes
read only = no
guest ok = no
valid users = "@domain admins@server2022.local"
vfs objects = acl_xattr
map acl inherit = yes
store dos attributes = yes
6. Directory Permissions & Services
Create the mount point and assign ownership to the Domain Admins group.
Bash
sudo mkdir -p /srv/samba/domain_share
sudo chown "administrator@server2022.local":"domain admins@server2022.local" /srv/samba/domain_share -R
sudo chmod +x /srv/samba
# Restart services to apply changes
sudo systemctl restart sssd smbd
7. Connecting from the DC (SBS.SERVER2022.LOCAL)
Since you are connecting from the DC itself, you must clear the Kerberos cache to avoid loopback authentication errors.
- Open PowerShell (Admin) on the DC.
- Run: klist purge
- Run: net use Z: \\172.27.176.32\DomainShare /user:administrator@server2022.local